Product Management And The Importance of Customer Centricity
An overview of customer centricity, its key aspects, and how we help our customers ace them in projects

Olga Medvedeva
24.1.2025
Do you remember what the photography market looked like 20 years ago? No smartphones, no digital cameras - only cameras with foils. At the end of the 1990s and the beginning of the 2000s, Kodak stood as a market leader, dominating the photography world with its iconic film products. Today, we remember the brand only when we happen to spot its iconic products in stores and feel nostalgic about using the cameras we liked some decades ago. So, what happened to Kodak? The company filed for bankruptcy in 2012. Despite inventing one of the first digital cameras, Kodak was hesitant to fully embrace digital technology, fearing it would destroy its profitable film business. By the time Kodak realized the importance of digital technology, it was already too late - its main competitors had already owned the market, leaving Kodak behind.
Customer Centricity
In our previous post, we introduced the agile mindset. Today, we will dive deeper into customer centricity and product management.
Peter Drucker, the famous management thinker, once said "The purpose of a business is to create and keep a customer".
Kodak's story highlights the consequences of losing sight of customers' evolving needs. Rather than adapting to the growing demand for digital solutions, Kodak clung to its outdated business model. By prioritizing short-term profits over long-term customer satisfaction, Kodak allowed its competitors to seize the market lead, ultimately leading to its decline. In other words, Kodak failed to prioritize customer centricity, which contributed significantly to its downfall.

What is customer centricity?
Customer centricity is a strategic approach that places the customer at the heart of a business's operations and decision-making. It focuses on deeply understanding and anticipating customer needs and preferences, and then delivering value through tailored products, services, and interactions. This approach is dynamic, continually evolving based on customer feedback and shifts in expectations. By prioritizing the customer experience and adapting to their changing demands, businesses can build lasting relationships, enhance satisfaction, and drive sustainable growth.
For professionals working with products and services - such as product owners, product managers, or software engineers - customer centricity is essential. It means prioritizing features that address user problems and enhance satisfaction. For software engineers, it involves designing intuitive and user-friendly experiences. Together, these roles ensure that solutions not only meet customer needs but also build loyalty and deliver exceptional value.
Agility is crucial for maximizing the benefits of customer centricity, as it allows teams to quickly adapt to evolving customer needs through iterative development and continuous feedback. This flexibility ensures that products remain relevant and aligned with market demands, enabling teams to deliver high-quality, customer-focused solutions efficiently. By embracing agility, teams can better respond to changes, innovate rapidly, and maintain a strong focus on customer satisfaction.
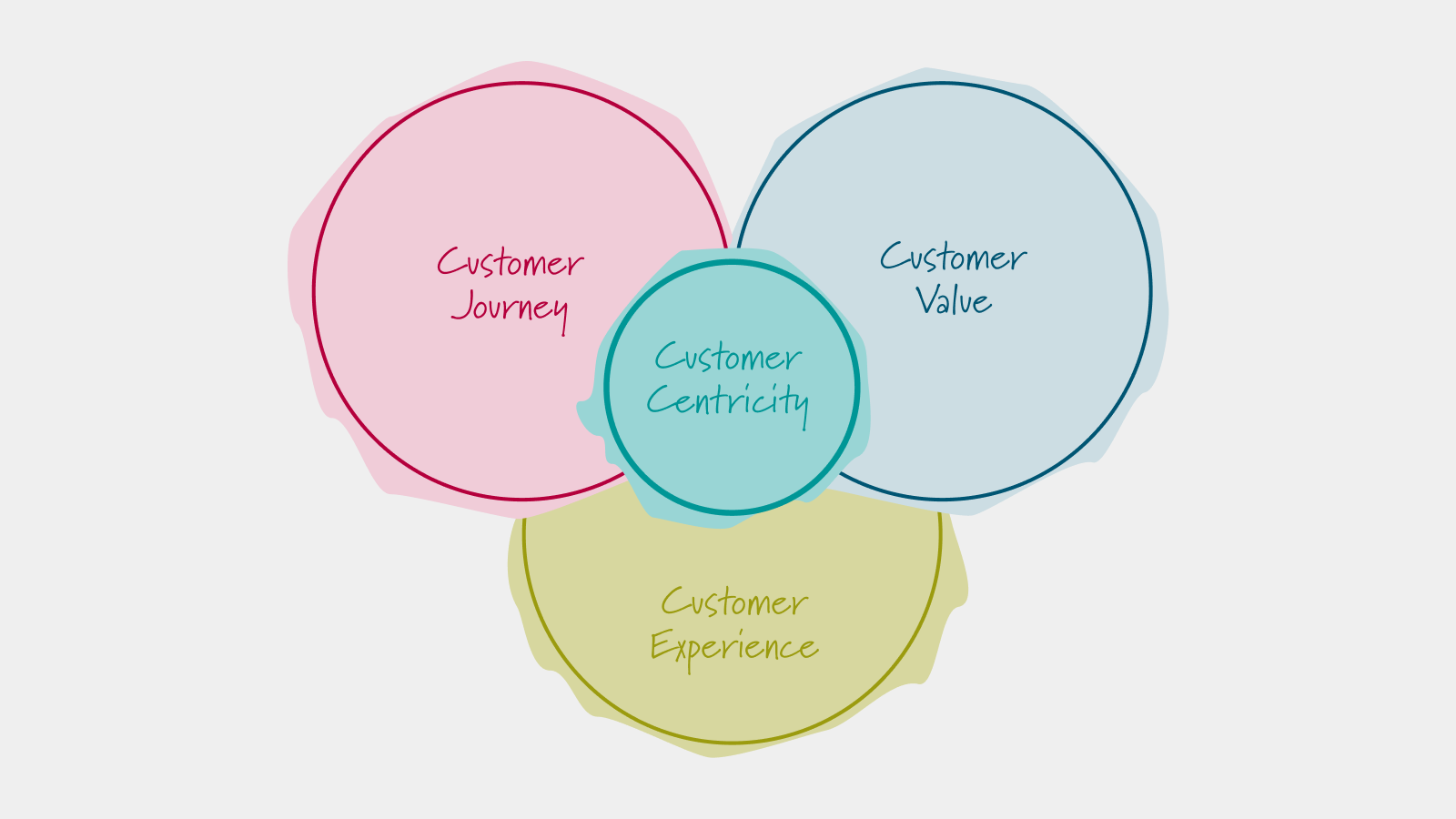
Customer centricity encompasses customer value, customer experience, and the customer journey, integrating these elements to create a comprehensive and satisfying engagement with clients.

1. Customer Journey
The customer journey focuses on understanding and enhancing the overall experience a customer has with a product or service through five stages: awareness, consideration, purchase, retention, and loyalty. Each stage represents different customer touchpoints, feelings, and thoughts, providing a comprehensive view of how customers engage with a brand over time.
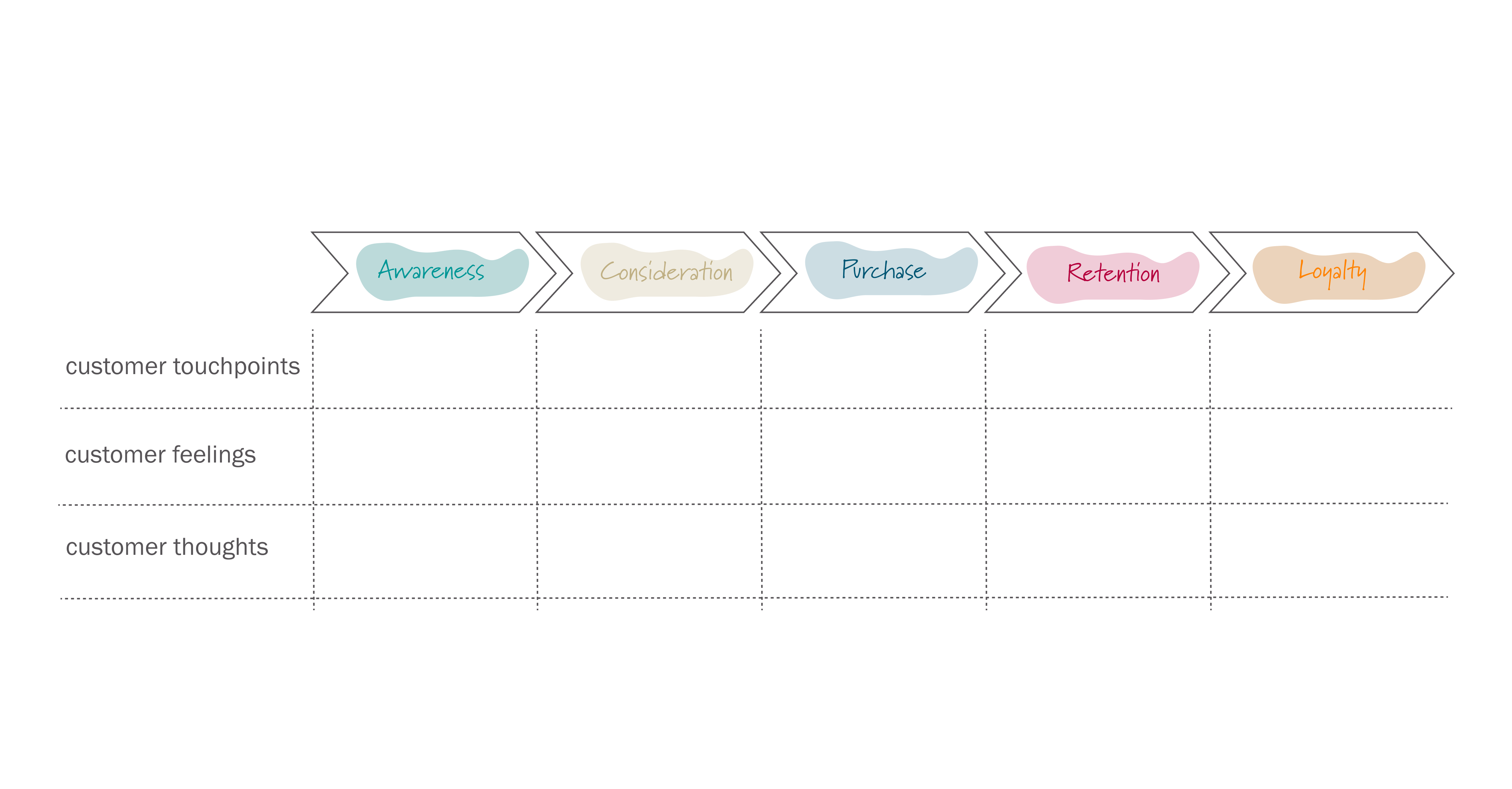
Mapping the customer journey helps a company identify key touchpoints and pain points, enabling it to optimize interactions, enhance satisfaction, and drive greater customer loyalty and retention.
Why does the customer journey often fail?
Lack of understanding of customer needs, inconsistent experiences across channels, and failure to adapt based on feedback are the most common reasons. Additionally, poor collaboration between teams and overly complex processes can frustrate customers and disrupt their experience.
In the agile world, iterative development, continuous collaboration, and adaptability to changing requirements ensure a dynamic and responsive customer journey. Agile practices enable teams to regularly refine each stage of the journey based on real-time feedback, quickly addressing pain points and enhancing touchpoints. This approach ensures that the customer experience is consistently aligned with evolving needs and market demands, resulting in improved satisfaction and loyalty.
2. Customer Value
Customer value is a fundamental element of customer centricity, reflecting the overall worth a customer gains from a product or service. The value encompasses the benefits, satisfaction, and positive experiences delivered while subtracting the costs incurred by the customer.
Focusing on creating high customer value fosters long-term competitive advantages, ensures sustained profitability in changing markets, and drives consistent success.
Companies generate value by enhancing the difference between willingness to pay (WTP) and willingness to sell (WTS).
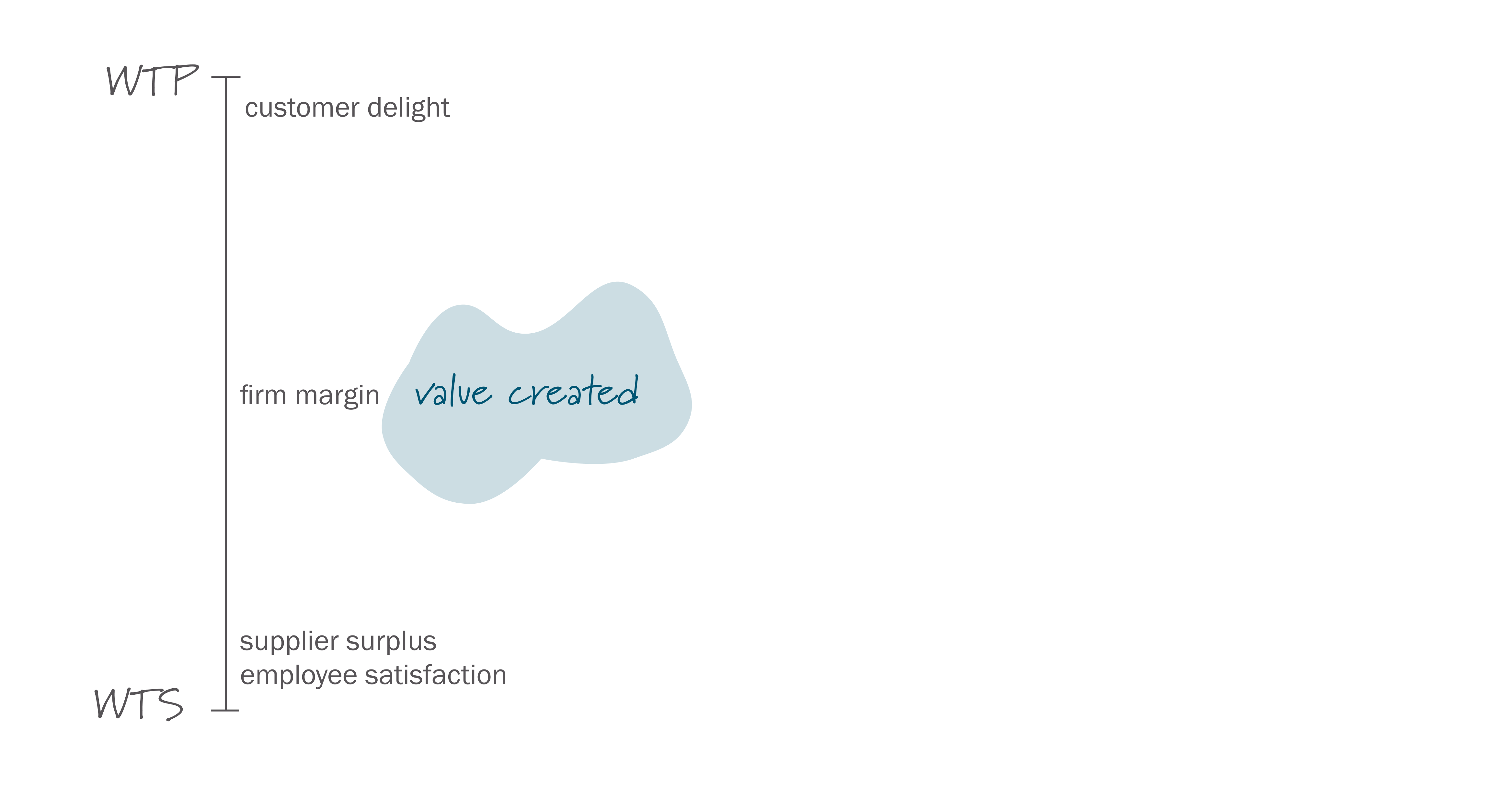
There are three ways to generate customer value:
- Enhance the difference between WTP and price: By increasing the perceived value relative to the cost, making the offering more attractive.
- Enhance the difference between employees' compensation and WTS: By ensuring that compensation aligns with the value created, thus motivating employees to contribute effectively.
- Enhance the difference between price and cost: By managing production and operational costs efficiently to increase profit margins while maintaining or improving customer value.
Why does value creation often fail?
The most common reasons for failure are the lack of innovations, oversight of changing market conditions, inconsistent customer experiences, inadequate customer support, and ineffective communication.
In an agile environment, value creation is influenced by continuous delivery, regular customer feedback, adaptability to change, and cross-functional collaboration. These practices help ensure that products and services remain aligned with customer needs and market dynamics, enhancing the overall value.
3. Customer Experience
Customer experience encompasses the overall interaction and satisfaction that a customer has with a product or service during its development and delivery. It is shaped by several factors such as understanding and addressing customer needs, creating emotional connections, fostering ease of use by developing intuitive user-friendly solutions, and providing support before and after the purchase. Additionally, ensuring personalized and seamless engagement across all touchpoints is essential.
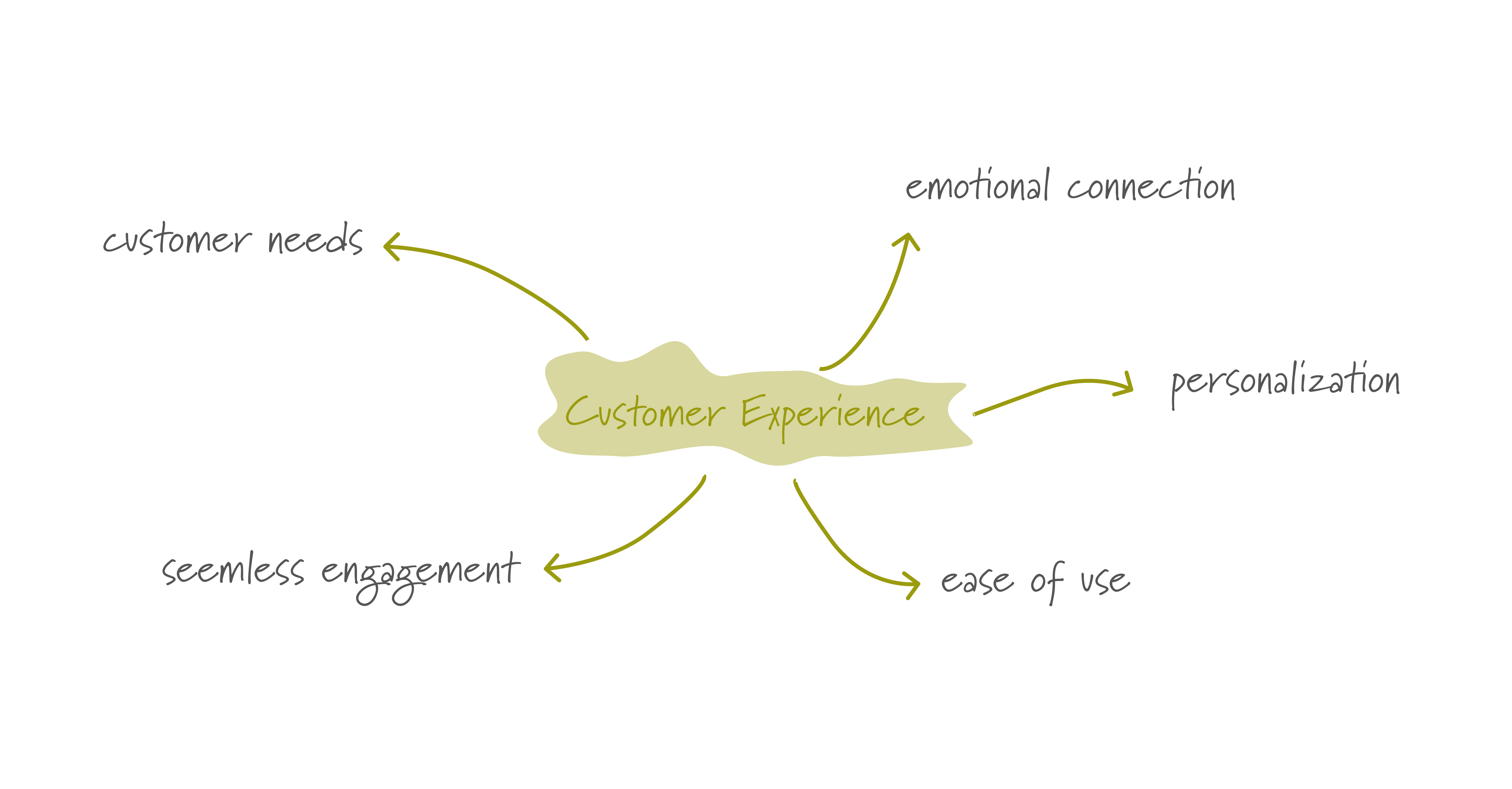
A strong customer experience enhances customer loyalty, drives repeat business, and boosts overall brand reputation, leading to increased revenue and sustained competitive advantage.
Why does customer experience often fail?
The most common reasons are a poor understanding of customer needs, lack of knowledge of persona, inconsistent interaction, and ignorance of valuable feedback.
In an agile environment, customer experience is optimized through iterative development, continuous collaboration, and rapid adaptation to evolving needs. This approach allows teams to regularly gather feedback, refine products, and respond swiftly to trends or issues. Agile practices promote a customer-first mindset, ensuring each iteration delivers value, enhances usability, and improves the overall experience. By fostering close collaboration between teams and customers, agility creates flexible, customer-centric solutions that adapt to market changes and exceed expectations.
Mapping the customer journey helps a company identify key touchpoints and pain points, enabling it to optimize interactions, enhance satisfaction, and drive greater customer loyalty and retention.
Why do companies fail in applying the customer journey?
Lack of understanding of customer needs, inconsistent experiences across channels, and failure to adapt based on feedback are the most common reasons. Additionally, poor collaboration between teams and overly complex processes can frustrate customers and disrupt their experience.
In the agile world, iterative development, continuous collaboration, and adaptability to changing requirements ensure a dynamic and responsive customer journey. Agile practices enable teams to regularly refine each stage of the journey based on real-time feedback, quickly addressing pain points and enhancing touchpoints. This approach ensures that the customer experience is consistently aligned with evolving needs and market demands, resulting in improved satisfaction and loyalty.
How Customer Centricity Failures Led to a Brand's Fall
Consider the example of Nokia... Two decades ago, this Finnish brand was dominating the market of mobile phones. Nowadays, the brand does not produce gadgets but focuses on telecommunication solutions.
Nokia’s decline from a market leader in mobile phones can be attributed to several key factors related to customer value, journey, and experience.
Firstly, Nokia’s focus remained heavily on hardware, neglecting the holistic customer experience that modern consumers demanded, such as sophisticated software and integrated services. This failure to innovate and align its touchpoints with emerging trends resulted in a diminished user experience compared to competitors.
Secondly, Nokia's inability to anticipate and adapt to rapid technological changes led to a disconnect in its value journey. While the brand initially excelled in generating awareness and engaging customers with its reliable feature phones, it struggled to convert and retain customers as the smartphone era emerged, leaving it behind in an evolving market.
Lastly, Nokia's slow integration of customer feedback and its inconsistent response to shifting expectations weakened its emotional connection with consumers. As competitors like Apple and Android introduced advanced features and more engaging experiences, Nokia's once-strong brand advocacy eroded, ultimately leading to its decline in the mobile phone market
Customer Centricity And The Experience of transentis
With over 25 years of expertise, we at transentis have developed a profound understanding of customer centricity and project success.
Through our extensive experience, we have identified recurring mistakes in managing customer centricity. To address these, we highlight common pitfalls and outline our strategies for overcoming them effectively.
1. Mapping The Customer Journey And Its Touchpoints
The customer journey is often a key consideration when companies work on internal services or tools. However, due to constraints like limited time or resources, the focus frequently shifts to building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP), sidelining a comprehensive customer journey process. As a result, many professionals overlook the critical importance of fully understanding and optimizing the entire customer experience from the start.
A few years ago, we worked with one of our clients on developing an internal tool for one of the services. Right from the start, we made the customer journey our top priority, regularly assessing it throughout the entire development process.
Initially, we focused on the key touchpoints in the customer journey while we were developing and refining the current process model. To identify these touchpoints, we conducted detailed interviews with users, gathering insights into their interactions with the product or service. This approach helped us uncover the feelings, thoughts as well as pain points of users.
After that, we refined the process model with the help of initial feedback. Then we reengaged with customers to validate our improvements through additional rounds of feedback. This iterative process ensured that both we and the client were continuously evolving the model in response to real user experience, resulting in a more effective design and improved customer satisfaction.
Finally, we implemented a continuous support system, enabling us to quickly identify and address any further necessary changes.
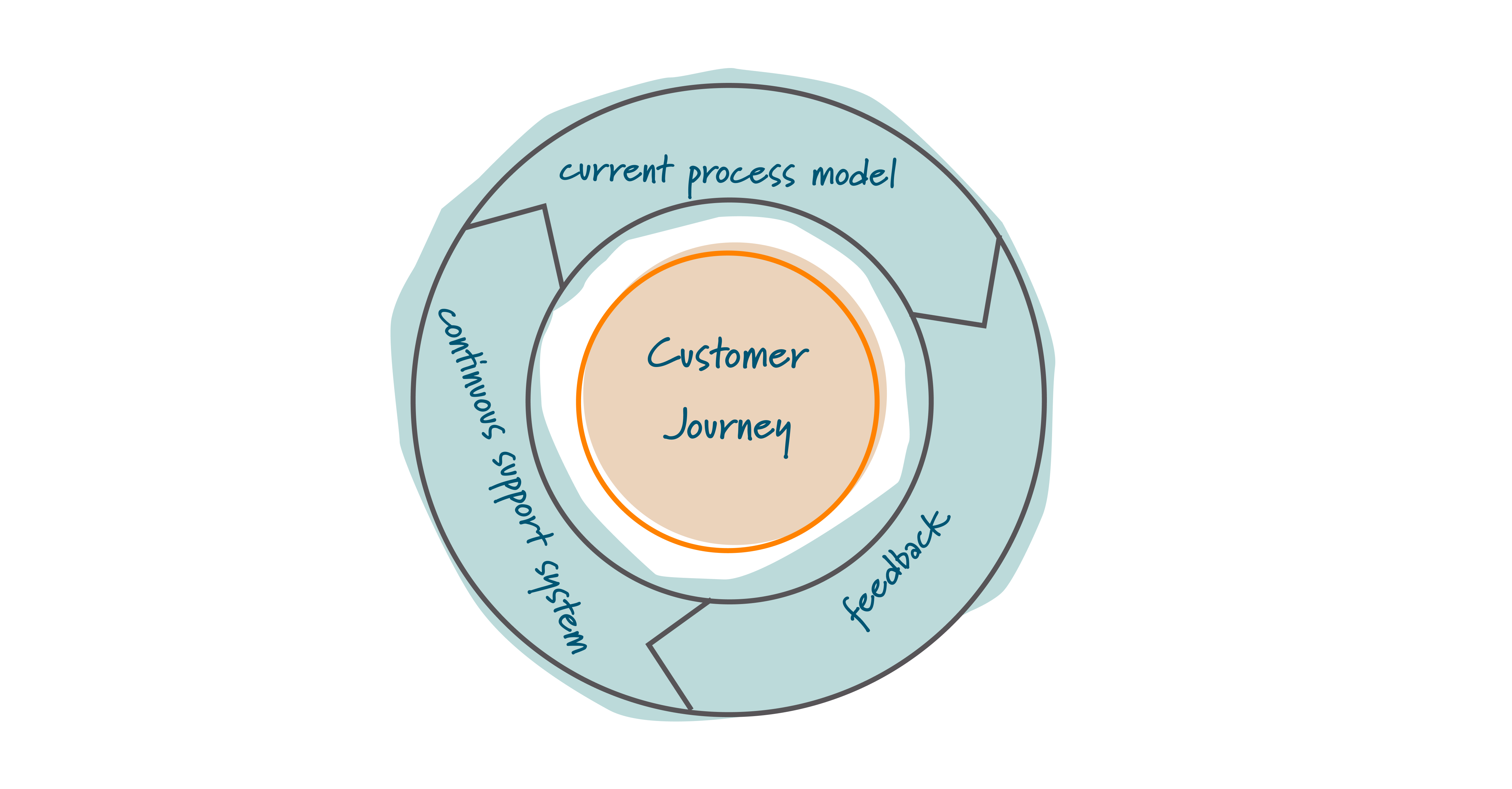
This approach has ensured that the customer journey remains optimized over time, providing lasting value to the client and their users.
2. Focusing on Customer Value and Prioritization within a Roadmap
Enterprises often underestimate task prioritization when they start working on projects. The larger the project - whether in terms of tasks or team members—the more critical effective prioritization becomes. Without it, coordinating efforts, managing resources, meeting deadlines, and delivering customer value can be extremely challenging. Consequently, the end product or service may fall short of expectations, either in quality or its ability to address the customer's needs.
At transentis, we recognize the pivotal role of prioritization and address it right from the outset of every project. The first two elements we focus on are stakeholder and customer engagement, along with resource allocation, to ensure we deliver optimal results.
First, we identify the core features that offer immediate value to the customer, assigning them the highest priority.
Next, we actively engage customers and stakeholders in numerous meetings to develop a clear roadmap that serves as a guide for all teams and outlines essential steps in the project's development.
After that, we ensure that features are properly aligned, adjusted, discussed, and evaluated, based on the effort required for implementation.
Throughout all three steps, we consistently validate customer value by interviews with various process stakeholders.
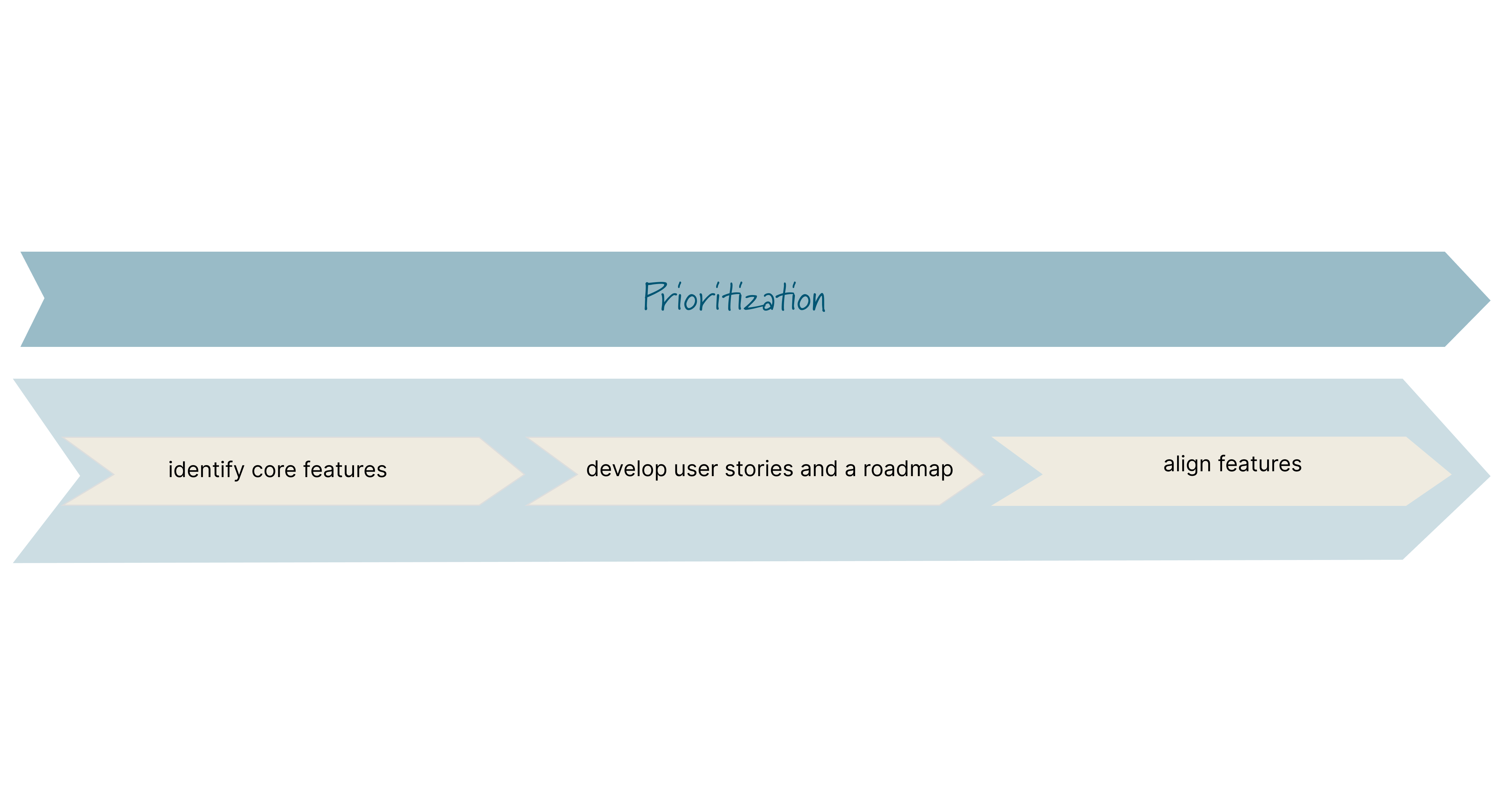
This approach ensures that the project stays aligned with customer expectations and delivers the best possible outcomes.
3. Enhancing Customer Experience And Integration
Quite often customers engage with a product or service only shortly before or after a launch of a product or service. This late-stage involvement can lead to integration issues that might have been avoided with more consistent participation from various stakeholders—such as developers, end users, and management—throughout the development process.
Recently, transentis consultants worked on a large project in the mobility sector. From the outset, we prioritized gathering customer feedback as frequently as possible.
First, we created and adjusted a process model which was displayed at every meeting to create a common understanding and visualize the underlying process logic. Already at this stage, we identified key workflows that helped us establish clarity and mutual understanding among all stakeholders.
Next, we organized user story meetings, where customers, developers, product owners, subject matter experts, and stakeholders took part. These sessions are essential for aligning feature requirements and setting priorities, ensuring that development efforts are focused on delivering the most valuable outcomes.
Finally, we conducted workshops at key project stages and brought together all the participants once again to gather their feedback in terms of experience. These workshops fostered collaboration, enabled early indication of challenges, and ensured that all essential components were integrated effectively.
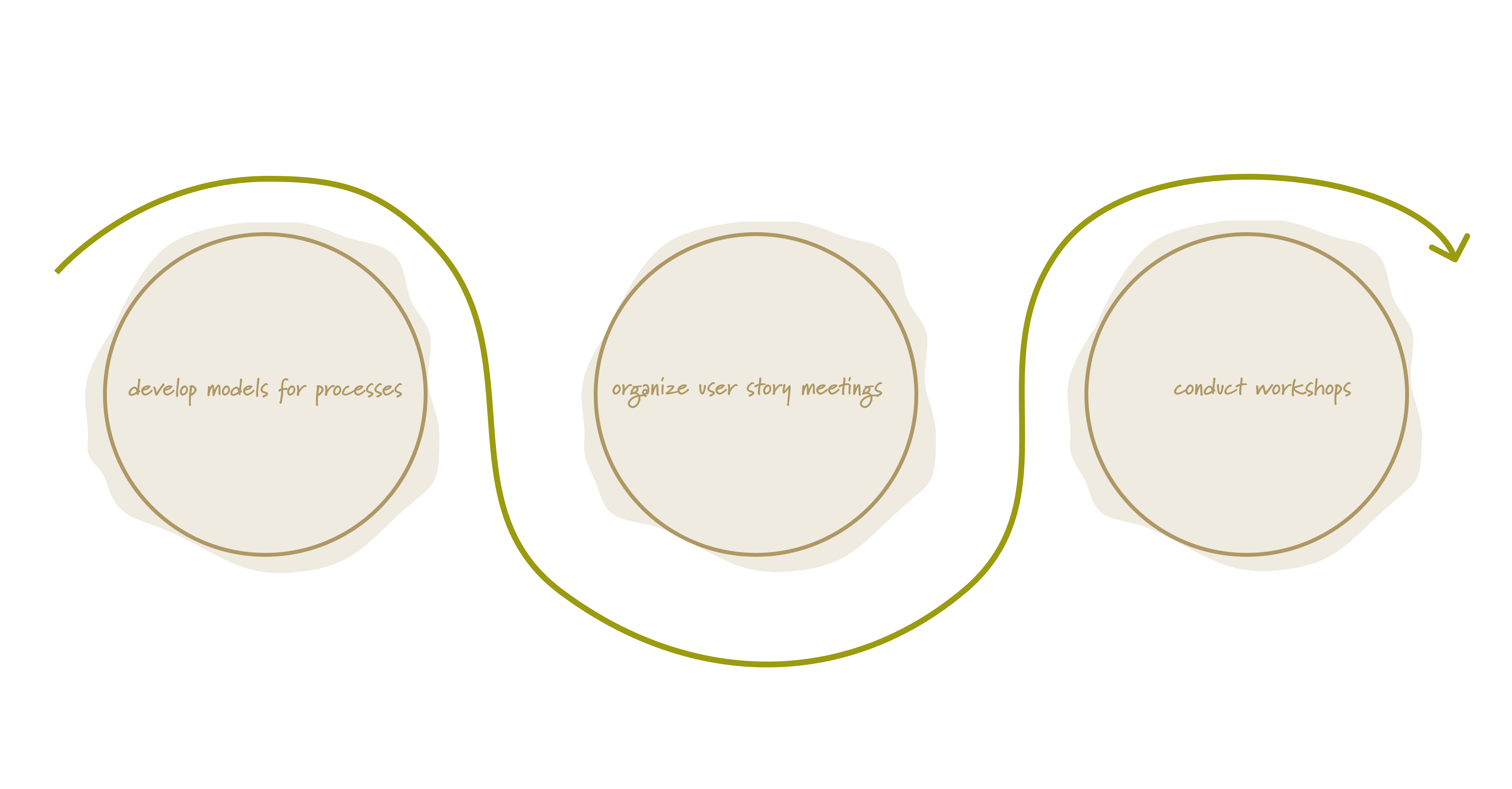
Collecting and working with customer feedback at various project stages enabled our customers to improve overall efficiency, enhance understanding, and drive the success of the project.
Conclusion
Focusing on customer journey, value, and experience is essential for sustained success in any product or service. The declines of Kodak and Nokia highlight the risks of ignoring evolving customer needs and technological advancements.
With over 25 years of expertise, transentis empowers clients to prioritize customer centricity effectively. This approach improves user satisfaction, optimizes processes, and drives success, ensuring that solutions not only meet but exceed customer expectations.
Table of Contents
Newsletter
Stay up to date about content and events.
Upcoming EventsEvents overview
Upcoming Events
Events overview
Workshops
Resources
All Rights Reserved.